Evidence based practice of Stroke in Occupational Therapy
ผู้รับบริการโรคหลอดเลือสมอง(Stroke)
ทฤษฎีและวิทยาศาสตร์
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับโรค ผลกระทบของโรคต่อการทำหน้าที่ของร่างกาย และกิจกรรมการดำเนินชีวิตของมนุษย์
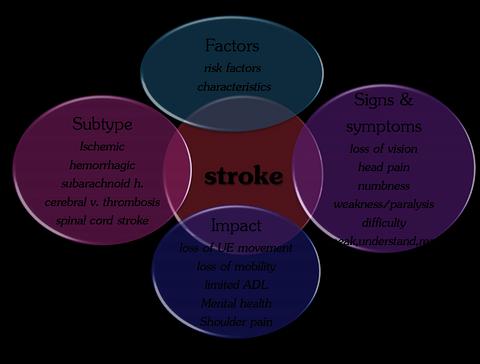
โรคหลอดเลือดสมอง(Stroke)
การจำแนก(Subtype)
- Ischemic
- hemorrhagic
- subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- cerebral venous thrombosis
- spinal cord stroke
ปัจจัยการเกิด(Factors)
- ปัจจัยเสี่ยง(Risk factors) ยกตัวอย่างเช่น การสูบบุหรี่,ความเครียด,ความดันสูง,ความอ้วน,กรรมพันธุ์ ฯลฯ เป็นต้น - ลักษณะบุคคล(characteristics) ยกตัวอย่างเช่น เป็นมากในอายุเฉลี่ยประมาณ 48 ปี, คนในเมืองเป็นมากกว่าคนนอกเมือง, คนที่แต่งงานแล้วเป็นมากกว่าคนโสด หรือหย่าร้าง, คนที่มีรายได้สูงเป็นมากกว่าคนที่รายได้ต่ำ ถึงปานกลาง เป็นต้น
ลักษณะอาการ(Signs & symptoms)
บกพร่องทางการมองเห็นข้างออนแรง(loss of vision), มีอาการปวดศีรษะ(head pain), อาการชา(numbness), อาการอ่อนแรง(weakness/paralysis), ยากลำบากในการพูด เข้าใจ และการอ่าน(difficulty in speak,understand,read)
ผลกระทบ(Impact)
- สูญเสียการเคลื่อนไหวของแขน และมือ
- บกพร่องในการเคลื่อนย้ายตนเอง
- มีข้อจำกัดในการทำกิจวัตรประจำวัน
- ส่งผลต่อสุขภาพจิต (ซึมเศร้า วิตกกังวล)
- มีอาการปวดไหล่ของข้างอ่อนแรง ซึ่งเกิดจากไหล่หลุด(Shoulder subluxation)
ที่มา : Sung Sug Yoon, Richard F. Heller, Christopher Levi, John Wiggers and Patrick E. Fitzgerald.Knowledge of Stroke Risk Factors, Warning Symptoms, and Treatment Among an Australian Urban Population.Stroke. 2001;32:1926-1930
P. Amarenco J. Bogousslavsky L.R. Caplan G.A. Donnan M.G. Hennerici.Classification of Stroke Subtypes.Cerebrovasc Dis 2009;27:493–501
การให้คะแนน PEDro scale ดังนี้
Internal Validity Score: 0/8 Statistical Reporting Score: 0/2
• Randomly allocated: No • Between-group comparisons: No
• Concealed allocation: No • Point estimates and variability: No
• Baseline comparability: No Eligibility Criteria Specified: No
• Blind subjects: No
• Blind therapists: No
• Blind assessors: No
• Adequate follow-up: No
• Intention-to-treat: No
การให้น้ำหนัก :(+/-) "อาจทำหรือไม่ทำ" เนื่องจากงานวิจัยนี้เป็นการวิจัยสำรวจของประเทศ Australia ซึ่งบริบทอาจแตกต่างจากประเทศไทย สามารถนำมาเป็นแนวทางในการได้ แต่ควรหาหลักฐานงานวิจัยจากประเทศไทยสนับสนุนเพิ่มเติมด้วย

ที่มา : Carla Sabariego.Andrea E. Barrera. Silvia Neubert. Marita Stier-Jarme. Cristina Bostan. Alarcos Cieza.Evaluation of an ICF-based patient education programme for stroke patients: A randomized, single-blinded, controlled, multicentre trial of the effects on self-efficacy, life satisfaction and functioning.The British Psychological Society 2012
การให้คะแนน PEDro scale ดังนี้
Internal Validity Score: 4/8 Statistical Reporting Score: 1/2
• Randomly allocated: Yes • Between-group comparisons: Yes
• Concealed allocation: No • Point estimates and variability: No
• Baseline comparability: No Eligibility Criteria Specified: No
• Blind subjects: Yes
• Blind therapists: No
• Blind assessors: No
• Adequate follow-up: Yes
• Intention-to-treat: Yes
การให้น้ำหนัก : (+) "น่าทำ" แม้ผลการวิจัยจะไม่แตกต่างกันอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ แต่หัวข้อ และรูปแบบการวิจัยมีความน่าสนใจ และเหมาะสมกับกรณีศึกษา ยังไม่ได้ผ่านการวิเคราห์ผ่านบริบทของไทยกระบวนการให้เหตุผลทางคลินิก
Randomized Trial of Distributed Constraint-Induced Therapy Versus Bilateral Arm Training for the Rehabilitation of Upper-Limb Motor Control and Function After Stroke
ที่มา :Ching-yi Wu. Li-ling Chuang. Keh-chung Lin. Hsieh-ching Chen. Pei-kwei Tsay.Randomized Trial of Distributed Constraint-Induced Therapy Versus Bilateral Arm Training for the Rehabilitation of Upper-Limb Motor Control and Function After Stroke.Neurorehabil Neural Repair.2011;(25)2:130-139
สรุป: ผลของเทคนิคการรักษาแบบ Distributed Induced Therapy กับ Bilateral Arm Training ไม่มีความแตกต่างกันมากนักขึ้นอยู่กับเป้าประสงค์ BAT จะได้ผลดีในการเพิ่มระดับแรงของแขน ส่วน Distributed Induced Therapy จะได้ผลในการเพิ่มความสามารถในการทำงานชีวิตประจำวันของแขนข้างที่อ่อนแรง ทั้งนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับการวางแผนของนักกิจกรรมบำบัดด้วย
การให้คะแนน PEDro scale ดังนี้
Internal Validity Score: 2/8 Statistical Reporting Score: 1/2
• Randomly allocated: Yes • Between-group comparisons: Yes
• Concealed allocation: No • Point estimates and variability: No
• Baseline comparability: No Eligibility Criteria Specified: Yes
• Blind subjects: No
• Blind therapists: No
• Blind assessors: No
• Adequate follow-up: Yes
• Intention-to-treat: No
การให้น้ำหนัก : (+) "น่าทำ" มีความเหมาะสมกับสถานการณ์และสถานภาพของการประกอบวิชาชีพในประเทศไทย และเนื่องจากทั้งสองเทคนิค เป็นที่นิยมในการรักษาทางคลินิกของนักกิจกรรมบำบัดในเมืองไทยด้วย ที่สำคัญเป็นเทคนิคที่กระผมใช้กับกรณีศึกษาทั้งสองเทคนิคความเห็น (0)
ไม่มีความเห็น